Understanding Copper Pipe Sizes for Air Conditioners

What size copper pipe for air conditioner should you use? Picking the right size is very important. It helps the system work well and last longer. Rules like ASTM B 280 explain what copper pipes need. Here are some main details:
Copper alloy C12200 must have at least 99.9% copper.
Phosphorous content should be between 0.015% and 0.040%.
Sizes begin at ¼ inch or bigger, with labels for coils and straight pipes.
These rules help your system run better and avoid refrigerant problems. The correct pipe size for air conditioner applications saves energy and improves efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Picking the right copper pipe size is very important. It helps refrigerant flow well and improves cooling.
Covering copper pipes with insulation saves energy and stops moisture damage. Good insulation keeps refrigerant at the right temperature.
Always follow the manufacturer's rules for pipe sizes. This helps the system work better and avoids refrigerant problems.
Use proper tools and methods to cut and connect pipes. This stops leaks and makes strong connections.
Check pipes and insulation often to see if they are okay. Fixing problems early saves money and keeps your AC working well.
Standard Sizes for Copper Pipes in Air Conditioning

Common Sizes and Their Measurements
Choosing the right copper pipe size is very important. It helps refrigerant move smoothly, making the system work better. Below is a table showing common sizes and their uses:
Size | Application Description |
|---|---|
1/4 inch | Best for small air conditioners or fridges. |
3/8 inch | Good for home cooling systems with medium needs. |
1/2 inch | Used in bigger HVAC systems for better cooling. |
5/8 inch | Great for commercial systems needing more cooling power. |
3/4 inch | Perfect for heavy-duty cooling in factories. |
7/8 inch | Works best for very large air conditioning units. |
Each size has a specific job to do. For example, 1/4 inch pipes are great for small systems. On the other hand, 7/8 inch pipes are made for big industrial cooling.
Applications of Standard Sizes in Air Conditioning Systems
Different pipe sizes are used for different cooling needs. Small pipes like 1/4 inch and 3/8 inch are common in homes. They handle light to medium cooling well. Medium pipes, such as 1/2 inch and 5/8 inch, are better for larger homes or small businesses. These sizes allow refrigerant to flow smoothly for steady cooling.
For factories or big buildings, 3/4 inch and 7/8 inch pipes are ideal. They can carry more refrigerant, which is needed for heavy cooling. Picking the right size keeps the system running well and protects the compressor from overwork.
Suction Lines vs. Liquid Lines: Key Differences
Copper pipes in air conditioners are either suction lines or liquid lines. Each type has a special job:
Suction Lines: These pipes bring low-pressure gas back to the compressor. They are wider to hold more gas. Correct sizing stops pressure drops and keeps the system efficient.
Liquid Lines: These pipes move high-pressure liquid refrigerant to the evaporator. They are thinner than suction lines. Proper sizing avoids clogs and keeps refrigerant flowing smoothly.
Here’s a table showing measurements for standard copper pipe sizes. It helps you see which sizes fit suction or liquid lines:
Nominal Size (inches) | Outside Diameter (inches) | Inside Diameter (inches) | Wall Thickness (inches) | Weight (pounds/linear ft) | Contents (cu ft/linear ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1/4 | 0.250 | 0.190 | 0.030 | 0.0804 | 0.00020 |
1/2 | 0.500 | 0.436 | 0.032 | 0.182 | 0.00103 |
3/4 | 0.750 | 0.680 | 0.035 | 0.305 | 0.00252 |
1 1/8 | 1.125 | 1.025 | 0.050 | 0.655 | 0.00573 |
2 1/8 | 2.125 | 1.985 | 0.070 | 1.75 | 0.0215 |
The chart below shows these measurements visually. It helps you compare suction and liquid lines:
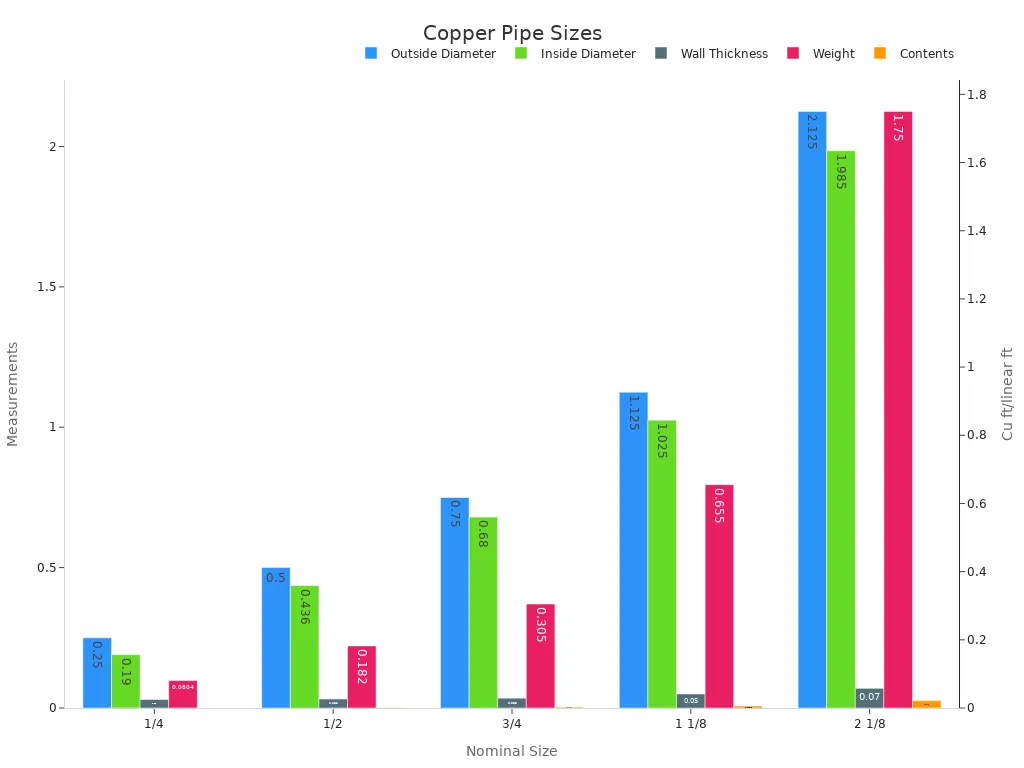
Knowing these differences helps you pick the right pipe size. This improves how well the system works and makes it last longer.
Factors Influencing Copper Pipe Size Selection
System Capacity and Load Requirements
The size of copper pipes depends on the system's cooling needs. Pipes must handle refrigerant flow without causing pressure drops. If pipes are too small, refrigerant may turn to gas early. This lowers cooling power and can freeze the coils. Pipes that are too big hold extra refrigerant, upsetting the system's balance.
To avoid these issues, think about your system's cooling load. Bigger systems need wider pipes for smooth refrigerant flow. Smaller systems, like those in homes, work well with narrower pipes. Picking the right size helps the system run efficiently and protects the compressor.
Energy Efficiency and Refrigerant Flow Considerations
Energy efficiency is key when choosing copper pipe sizes. Correctly sized pipes let refrigerant flow at the right speed. Small pipes cause pressure drops, making the compressor work harder. This uses more energy and shortens the system's life. Large pipes slow refrigerant flow, reducing cooling and heat transfer.
The type of refrigerant also affects pipe size. Different refrigerants flow differently, so choose pipes that match your system. Balancing refrigerant flow and pipe size improves energy use and lowers costs over time.
Tip: Check refrigerant levels and pipe condition regularly. This keeps your system efficient and working well.
Matching Pipe Size with Air Conditioning Unit Specifications
Choosing the right copper pipe size for your unit is important. Manufacturers give guidelines for the best pipe sizes. Following these ensures good cooling and avoids pressure problems.
When installing pipes, use proper tools for cutting and fitting. Secure connections through soldering keep the system leak-free. Pressure tests confirm the pipes can handle refrigerant safely. Supporting pipes with structures prevents damage over time.
Using the correct pipe size boosts efficiency and extends the system's life. Follow manufacturer advice and install pipes properly for the best performance.
Importance of Thermal Insulation for Copper Pipes

Stopping Energy Loss with Good Insulation
Thermal insulation is very important for copper pipes in air conditioners. Without it, heat moves between the refrigerant and the outside air. This wastes energy and lowers the system's cooling ability. Insulated pipes keep refrigerant at the right temperature. This helps the system cool better and use less energy.
Insulation also stops water from forming on pipe surfaces. Water can cause rust and mold, which damage the pipes. In cold weather, insulation keeps pipes from freezing and breaking. This prevents expensive repairs. By reducing heat loss or gain, insulation saves money and makes the system more energy-efficient.
Common Materials for Pipe Insulation
Picking the right insulation material helps save energy. Below is a table showing a study on materials that reduce heat loss:
Component | Description |
|---|---|
Inner Tube | Smooth red copper tube, 32 mm outer diameter, 2 mm wall thickness |
Outer Tube | Acrylic tube, 100 mm outer diameter, 5 mm wall thickness, 500 mm length |
Insulation | 20-mm-thick rubber plastic insulation material wrapped around the outer wall |
Purpose | Decrease heat transfer loss in the thermal energy storage unit |
Rubber plastic insulation is strong and keeps out moisture. Foam and fiberglass are also good choices because they block heat well. The best material depends on your system and local weather.
Tips for Insulating Copper Pipes
Good insulation keeps your air conditioner working well. Follow these steps to do it right:
Check pipes for old or damaged insulation.
Pick insulation based on your system and weather.
Measure pipes and cut insulation to fit.
Seal edges with glue or tape.
Wrap insulation tightly around pipes.
Use tape or clips to hold it in place.
Cover joints with extra insulation or special tape.
Add weatherproofing for outdoor pipes.
Inspect the work after finishing.
Keep notes about the insulation for later use.
Check insulation often for damage or moisture. Fix or replace bad parts quickly to stop energy waste. These steps protect your pipes and make your air conditioner work better.
Installation Considerations for Copper Pipes
Techniques for Cutting and Fitting Copper Pipes
Cutting and fitting copper pipes must be done carefully. Using the right tools helps avoid damage and ensures good connections. Follow these simple tips:
Use a junior hacksaw for small pipes under 12 mm wide. For bigger pipes, a tube cutter works better.
For very large pipes, use a fine-toothed hacksaw or power tools like circular saws. Sharp tools prevent pipe bending or breaking.
Cut pipe ends straight and remove rough edges inside and outside. This keeps joints strong and refrigerant flowing smoothly.
When using a tube cutter, avoid squeezing the pipe too much. This can weaken the joint and cause flow problems.
Before soldering, cut pipes straight, clean edges, and apply flux. Soldering is the most common way to join copper pipes in air conditioners.
These steps make sure your installation is safe and works well.
Avoiding Common Installation Errors
Mistakes during installation can cause expensive repairs later. Pay attention to these common problems to avoid them:
Defective Pipes: Check pipes for hidden flaws before using them. Flaws can lead to leaks.
Improper Handling: Don’t bend or stretch pipes too much. This can create weak spots that crack over time.
Incorrect Sizing: Always match pipe size to the system’s needs. Wrong sizes can block refrigerant flow and lower efficiency.
Fixing these issues helps your air conditioner last longer and work better.
Challenges in Retrofitting or Replacing Copper Pipes
Replacing or upgrading copper pipes can be tricky. Problems often involve costs, materials, and rules. Here’s a quick summary:
Problem | Details |
|---|---|
High cost of pure copper pipes | Pure copper pipes cost 8–12% more, raising project expenses. |
Thin walls increase failure rates | Pipes with thin walls break 12% more often, based on a 2022 study. |
Poor materials in some regions | Low-quality pipes in places like Vietnam cause more leaks. |
Expensive rules | Meeting rules adds $15,000–$20,000 per shipment in South Africa. |
Lower performance in local pipes | Pipes in places like Ghana work 23% worse than European-grade pipes. |
Knowing these problems helps you plan better for replacements. This ensures your system stays reliable for years.
Picking the right copper pipe size is very important. It helps refrigerant move easily and avoids pressure problems. This makes the system work better and last longer. Adding insulation stops energy waste and keeps pipes safe from harm. Using proper installation methods prevents leaks and helps the system last.
Tip: If the job seems hard, ask an expert. They can make sure your system works well and stays safe.
Paying attention to these details improves your air conditioner’s performance. It also helps you save money on energy bills.
FAQ
What happens if I use the wrong copper pipe size?
Using the wrong pipe size can cause refrigerant flow issues. This lowers cooling and might harm the compressor. Always choose the right size for your air conditioner to work well.
How do I know which pipe size my air conditioner needs?
Look at the manufacturer's instructions for your air conditioner. These guidelines list the correct pipe size based on cooling needs and refrigerant type. Following them ensures your system works properly.
Can I reuse old copper pipes when replacing my air conditioner?
You can reuse old pipes if they are in great shape. Check for rust, leaks, or damage first. If you're unsure, ask a professional to avoid problems later.
Why is insulation necessary for copper pipes?
Insulation stops energy loss and keeps refrigerant at the right temperature. It also prevents water buildup, which can cause rust or mold. Good insulation helps the system last longer and work better.
Are there alternatives to copper pipes for air conditioners?
Yes, aluminum pipes can be used instead of copper. They are cheaper and lighter but not as strong. Copper is still the best choice because it lasts longer and works better.
Tip: Always ask an HVAC expert for help with pipe selection and installation. This ensures your system runs efficiently.
See Also
Understanding Copper Pipe Dimensions: An In-Depth Overview
The Benefits of Selecting Copper Pipes for AC Systems
Exploring the Development of Copper Tubing in HVAC


